DapuStor’s 122TB Gen5 QLC SSD: Pioneering High-Density AI Storage
As AI technology evolves at breakneck speed, the industry is witnessing an unprecedented explosion of data. The bottleneck in AI infrastructure is shifting—no longer solely about compute power, but about how data is stored, accessed, and scaled. The critical challenge now lies in managing ever-growing volumes of warm and hot data with higher density, lower power consumption, and optimized total cost of ownership (TCO). Traditional expansion strategies are hitting limits in space, power consumption, and cost efficiency, prompting a new wave of infrastructure transformation—ushering in the era of enterprise-grade QLC SSDs.
As one of the Global Tier-1 Leaders in ultra-capacity enterprise QLC SSDs, DapuStor has launched its second-generation QLC solution this year: the PCIe Gen5 R6060 SSD. With a maximum capacity of up to 245TB and 122TB models already deployed by end customers, the drive is purpose-built and ideally suited for AI-Grade Data Lakes, vector databases, and large-scale storage scenarios. Entering this new phase, DapuStor brings to market a more mature QLC technology that delivers a compelling balance of performance, energy efficiency, and cost-effectiveness for the AI era.
Why QLC, and Why Now?
01 Overcoming the Historical Barriers of QLC NAND
The critical timing for QLC adoption hinges on two convering forces: the maturation of NAND architecture and the evolving structure of AI-driven data. QLC NAND, which stores four bits per cell, delivers a significant increase in wafer utilization—boosting density by over 30% compared to TLC. While QLC once faced barriers from enterprise use due to concerns around endurance, performance, and write amplification, these limitations are now being resolved. Advancements in process technology, smarter firmware algorithms, and architecture-level data management have enabled QLC to meet the demands of large-capacity, enterprise-class workloads.


02 HDD Limitations in AI Workloads and the Shift Toward Modern Storage Architectures
The demand is also driven by end users. As training datasets grow and inference pipelines involve increasingly larger volumes of embeddings, log data, and video streams, data retention cycles extend, and retraining becomes more frequent. Meanwhile, energy consumption and TCO remain top cost concerns for enterprises.
Under these pressures, organizations need more than just large-capacity interface—they require a high-density, always-on “data foundation” that delivers consistent random I/O performance and can operate reliably at scale.
HDDs have traditionally dominated the capacity tier in data centers due to their advantage in storage density. However, their limitations are increasingly exposed in AI scenarios. Petabyte-scale datasets consume excessive rack space, while rising power and cooling demands challenge operational efficiency. More critically, mechanical HDDs fall short in supporting the random, mixed I/O patterns of AI training and inference workloads.
Adding to this paradigm shift, data structures in the AI era are transforming. Cold archival data is giving way to warm and hot data—dynamic assets that are frequently accessed or cyclically retrieved. This trend accelerates the need for dense, high-performance flash storage as the new backbone of AI infrastructure.
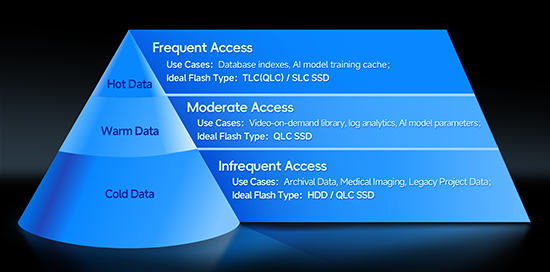
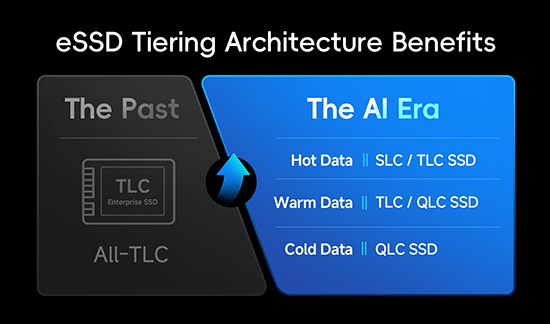
03 From All-TLC to SLC/TLC + QLC: The New Architecture Consensus
For over a decade, enterprise SSDs have relied predominantly on TLC NAND—offering a balanced trade-off between performance, endurance, and cost. It was the default choice for general-purpose workloads.
But the AI era reshapes this equilibrium. The rapid rise of warm and hot data means that all-TLC solutions are no longer sufficient to meet the combined demands of scalability, power efficiency, and cost-effectiveness.
The industry has responded with a new consensus: enterprise storage is moving away from single-tier TLC toward a multi-tiered architecture combining SLC/TLC for performance-sensitive workloads and QLC for high-capacity, read-intensive applications.

DapuStor 122TB QLC Gen5 SSD: Higher Capacity, Lower TCO
DapuStor has been a long-time pioneer of QLC technology and continues to invest in R&D across key areas such as system architecture, controllers, and firmware algorithms. The new R6060 SSD takes a major step forward in next-generation storage for AI workloads. Building on the proven architecture of the J5060, the R6060 brings a full-stack upgrade in the Gen5 era.
Powered by DapuStor’s PCIe 5.0 DP800 controller, the R6060 significantly boosts performance, delivers TLC-class performance fidelity at QLC Scale. It also introduces FDP (Flexible Data Placement) to minimize write amplification—ensuring stable performance and endurance even at 100+TB QLC capacity. With further improvements in unit cost, the R6060 enables a more competitive TCO for hyperscale deployments.

As AI scales, data will only continue to grow exponentially. The industry no longer needs just “faster” storage—it needs scalable, power-efficient, and cost-controlled infrastructure that can carry this growth forward. DapuStor is doubling down on QLC, strategically laying the foundation for petabyte-scale storage in the AI era.
About DapuStor
DapuStor Corporation, founded in April 2016, specializes in enterprise solid-state drives (SSDs), SoCs, and edge computing products. With a world-class R&D team of over 400 members, the company has comprehensive capabilities from chip design to mass production. DapuStor’s products are widely used in servers, telecom operators, and data centers, empowering businesses worldwide to manage their data more efficiently.
For more information, please contact:
Email: mkt@dapustor.com
Website: http://www.dapustor.com/
